Device iotlb: Difference between revisions
From KVM
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* Architecture independent: The implementation should be compatible to current Qemu's IOMMU architecture, then it should be architecture independent and then be easy to be ported to various platform/IOMMU implementation. | * Architecture independent: The implementation should be compatible to current Qemu's IOMMU architecture, then it should be architecture independent and then be easy to be ported to various platform/IOMMU implementation. | ||
* Efficient for dpdk like program: End user should have no obvious felling performance degradation when using dpdk like program in guest. The design was optimized for dpdk like programs which use fixed mappings in guest. | * Efficient for dpdk like program: End user should have no obvious felling performance degradation when using dpdk like program in guest. The design was optimized for dpdk like programs which use fixed mappings in guest. | ||
* Compatible: The implementation should be compatible | * Compatible: The implementation should be compatible with current vhost-net memory region API to support VM without DMAR enabled. | ||
== Design == | == Design == | ||
Revision as of 04:27, 4 February 2016
Vhost-net Device IOTLB
Overview
This page provides information about the design of Device IOTLB for vhost-net to provides a secure and efficient environment for dpdk like program in guest.
Design Goals
- Architecture independent: The implementation should be compatible to current Qemu's IOMMU architecture, then it should be architecture independent and then be easy to be ported to various platform/IOMMU implementation.
- Efficient for dpdk like program: End user should have no obvious felling performance degradation when using dpdk like program in guest. The design was optimized for dpdk like programs which use fixed mappings in guest.
- Compatible: The implementation should be compatible with current vhost-net memory region API to support VM without DMAR enabled.
Design
- Vhost-net can query the address mappings from guest io virtual address to host virtual address through ioctl.
- The above translation result could be cached in a vhost device specific IOTLB for a while to speed up the future translation in the future.
- Qemu can invalidate one or more mappings that cached by vhost through ioctl.
- Qemu can start or stop the DMAR through ioctl.
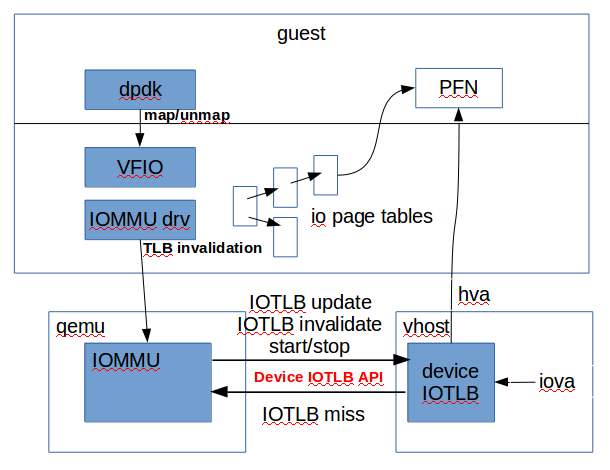
Example
- The above figure shows the design of device IOTLB for vhost-net:
- Startup:
- When DMAR was enabled by guest IOMMU driver, qemu will notify vhost to start the device IOTLB. Device IOTLB will be started with no entries cached.
- DMA emulation:
- When vhost tries to emulate a DMA, it will first tries to translate the guest iova to hva through device IOTLB.
- If vhost could not find a such translation, it will suspend itself and ask for the assistance of qemu to do the translation.
- Qemu get notified and will query the IOMMU for the translation.
- After the translation is finished, qemu will send the result to vhost.
- Vhost will then restart the DMA.
- TLB Invalidation:
- Vhost will snoop the TLB invalidation emulated by qemu.
- If a specific TLB invalidation is relate to the device whose DMA is emulated by vhost, vhost will be notified and the TLB entry cached by vhost will be cleared.
- Startup: